AUTOMATIC E-BABY CRADLE SWING BASED ON BABY CRY.
My latest Arduino DIY project is Automatic
E-Baby Cradle Swing based on Baby Cry.
Parents in the present world are busy in their professional
life, so they do not get sufficient time to take care of their babies. It may
be expensive for the household to afford a nanny.
Today’s woman has to manage home along with their office
work simultaneously. After long working hours, they have to take care of the
home along with the baby. They may not get enough time to swing the cradle
manually and sooth the baby. Moreover, in today’s life style, it is very difficult
even for the housewives to sit nearby their infants and sooth them whenever
they cry. Enhancing sleep quality is an important research topic, as quality
sleep is important for everyone, especially for infants . A comfortable
electric cradle with a low power consumption that can letinfants fall asleep
quickly is desired by many parents and numerous novel inventions based on swing
mechanisms in the form of springs or rods have been developed .Hospitals have
neonatal and maternity units. Nurses in these units have to take care of baby
and sooth them whenever they cry.
The system is designed to help parents and nurses in infants
care. The design aims at following points:
1.
Cradle starts swinging automatically when baby
cry and swings till the baby stops crying.
Sends message to mother’s mobile when
baby cries for more than a stipulated time indicating that baby needs
attention.
HARDWARE EXPLANATION:-
GSM module
Audio sensor KY-038
SERVO MOTOR
Arduino uno
Cradle (model)
Resistors
capacitors
MORE IMAGES
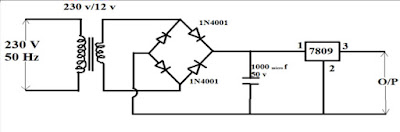
POWER SUPPLY DESIGN
use;Arduino uno
Arduino ide; http://www.arduino.org/downloads
Arduino coding handled by :- PRANAV S NAIR (pranavsnair93@gmail.com)
Project helping courtesy:- Felix philip <felixphilip86@gmail.com>
Project helping courtesy:- Felix philip <felixphilip86@gmail.com>
CODE
#include <Servo.h>
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
SoftwareSerial mySerial(9, 10);
int sensorPin = A0; // select the input pin for the potentiometer // select the pin for the LED
int sensorValue = 0;
int count=0;// variable to store the value coming from the sensor
int motor=8;
int motor2=10;
void setup ()
{
Serial.begin (9600);
mySerial.begin(9600); // Setting the baud rate of GSM Module // Setting the baud rate of Serial Monitor (Arduino)
delay(100);
pinMode(motor,OUTPUT);
pinMode(motor2,OUTPUT);
}
void loop ()
{ delay(200);
sensorValue = analogRead (sensorPin);
Serial.println (sensorValue, DEC);
if(sensorValue > 65)
{ digitalWrite(motor2,LOW);
digitalWrite(motor,HIGH);
delay(400);
digitalWrite(motor,LOW);
digitalWrite(motor2,HIGH);
delay(400);
}
else
{
digitalWrite(motor2,LOW);
digitalWrite(motor,LOW);
}
if(count>5)
{
if (Serial.available()>0)
switch(Serial.read())
{
case 's':
SendMessage();
break;
case 'r':
RecieveMessage();
break;
}
if (mySerial.available()>0)
Serial.write(mySerial.read());
}
}
void SendMessage()
{
mySerial.println("AT+CMGF=1"); //Sets the GSM Module in Text Mode
delay(1000); // Delay of 1000 milli seconds or 1 second
mySerial.println("AT+CMGS=\"+919995856777\"\r"); // Replace x with mobile number
delay(1000);
mySerial.println("baby is crying..!");// The SMS text you want to send
delay(100);
mySerial.println((char)26);// ASCII code of CTRL+Z
delay(1000);
}
void RecieveMessage()
{
mySerial.println("AT+CNMI=2,2,0,0,0"); // AT Command to receive a live SMS
delay(1000);
}